
More on Technology
Innominds and Qualcomm Collaborate to Drive Enterprise Digital Transformation with High-Compute Edge AI Platform
-
Team Eela
Master Data management is all about improving consistency and quality of your data organization wide. The necessity of the MDM arose with exponential growth of the amount of data that business handles, which is not only huge in size but also degrades very quickly. As per the research by D&B (Dun & Bradstreet) data degrades 27% per year and 61% in 2 years and in third year your data will not be usable at all.
The problem of bad data is gets even severe for big organizations as the amount and type of data they deal gets much more complicated as compared to small and medium size organizations. As per the research of HBR (Harvard Business Review) the bad data cost 3 trillion dollar per year in United states alone, just imagine its global impact.
The primary reason it happens is the inconsistency of the same data between multiple systems and frequent updates in the data. Other reasons are also possible like typo errors by the clients, customers, employees, and others, all of which contribute to the data degradation. Multiple business systems dealing with the same entity (Like customer, product, supplier, etc.) have different data.
Solution of this problem is master data.
Master data also referred to as a golden record in the world of data. Master data is a subject data belonging to a broader domain in the organization, which acts as a single source of truth for all the systems dealing with that data. The master data is centralized data for the whole organization managed and updated as per the company’s MDM protocols.

Master data is categorized as per the different domains of the organization or project. Like patients, diseases, equipment, supplies, etc. is suitable data domains for health care organizations. But master data is also not easy to manage because making a common standard or policies for maintaining the master data is also very strenuous work. This is because having buy-in from all the departments is not an easy task, as every department deals with data in way suitable for their efficiency.
Things begin with proper understanding and agreement of the importance of having master data and how the various department should operate on it. This does take us back to the first step of building a data strategy, where we discussed creating a Buy-in proposal so that everyone is in line for the task and have the necessary funding and participation needed for execution.
Master data management is the master mind behind the master files in the company. MDM brings the rules and regulations on managing and updating the master file. Master files are the central repository of the all the data like products, customer, demographics, asset, etc. These files are like the central truth data, accessed and used by all the departments or users in the company for operational and analytical processing.
All the master files are managed by the MDM system. The master data management system aims to make the messy and inconsistent data to a usable and reliable data, enhancing the accuracy and removing redundancy (Discussed in details down the lines). MDM not only maintains the master files but also comply with the regulatory mandates by like Sarbanes-Oxley Act (known as SOX), California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and most widely used, European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
All the departments have their respective data in an organization, which might even be interrelated unknown to their knowledge. These data are being used and handled by many applications and systems (Like ERP, CRM, etc.), most common issue faced by the users here is that the data becomes duplicated, fragmented and most commonly it gets outdated with time. After which, getting analytics, query results and predictions become highly unreliable and difficult to achieve.

Rate of data degradation is already discussed, this high rate is a result of many factors which cannot be changed. For Eg. typo errors made by the customer or employee, frequent updates of the status of the individuals like address, employment status, etc. and several other similar type of changes with the other business entities related to products, services, internal management. This makes data degradation a permanent enemy.
Master data helps each department be more effective in their operation by providing more accurate and updated data. This also helps the departments in increasing their collaborative effort in the project. The MDM also helps to implement the data governance rules and monitors any violation of the same.
Apart from the business Master data management’s operational advantages, it also enhances the analytical processing, query result, and prediction using ML models. By direct feeding the master files in the analytical systems like Data warehouses, the output analytics provides a complete picture of the customers, helping the companies make intelligent decisions and boost their marketing strategies.
Master data management does the following things for your data
It improves the data quality of the master files: This is the primary aim of any master data management system, Irrespective of its usage and architecture type. The aim here is to maintain the data’s consistency and reliability, which could be represented as a single source of truth (SSOT) to both operation processes and analytical processes.
It streamlines data sharing among various business platforms: Master files makes the data sharing and shifting among different platforms seamlessly, which reduces the time of acquiring the data from some company or project working on another platform.
Facilitates data transactions between the department: Data transactions are managed and updated centrally over the master files and all this is done as per the regulatory mandates and data governance policies implemented in the system.
MDM architecture is generally categorized in two domains, the core concept of maintaining the consistency and quality of the data and complying with the regulatory mandates and Data governance rules remains the same. The main difference between the two lies in use of the master data, which is transactional/ operational processing and analytical processing.
Maintaining the data quality of the master files is done by first integrating the data form the various source systems, after which data cleaning is done (Like removing duplicate files and merging them together, removing the incorrect and incomplete data files, etc.). After proper data validation and organization, data we achieved is known as the golden data or master data. The accessibility of this golden data is provided as per the governance and other regulatory mandates in the MDM program.
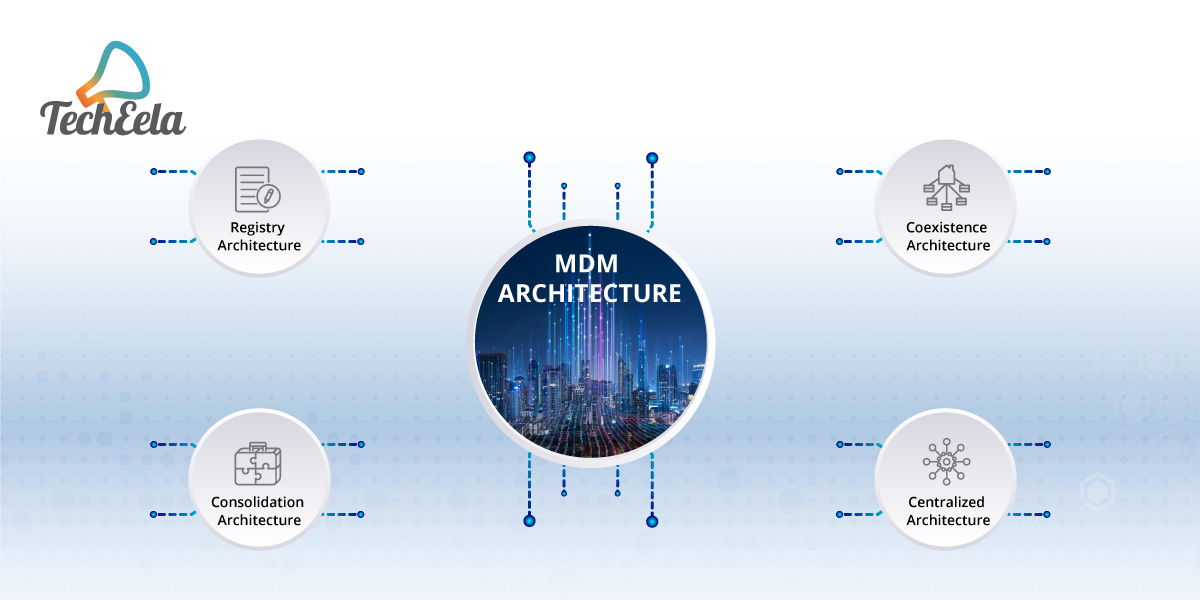
The different MDM architecture approach is based on the needs of the organization, which depicts how the hub will the MDM be connected to the source systems. These are the most commonly known ways to architect the enterprise master data management system:
Registry architecture: It is also referred as the most light weight MDM architecture. In this the master data is uniquely indexed in the registry, pointing to the source systems itself, which is used for analytical processing. Here the data cleaning is done by using matching tools for checking the duplicate files and reference.
Consolidation architecture: In this method, we consolidate the data from the sources systems to a central hub, known as the MDM hub. This centralized repository is used for analytical processing, BI and answering queries. Though the master data is copied in the hub, all sources system continues to only work on their system data.
Coexistence architecture: As its name suggests, In this method we also have the consolidated MDM hub but here when the user make changes in the master data file present in his system, it is also updated in the MDM hub, which is can be propagated to the other source systems om their demand. This architecture provides a balance between the centralized governance of master data and system-level management of master data.
Centralized architecture: Here all the management and updated master data is uploaded to the MDM hub. Through the hub all the source system gets the updates of the data files. This architecture provides the highest level of enterprise control but is also considered the most intrusive type of MDM from an enterprise point of view.
Master data management software, is also provided by the vendors that can be customised as per your organisation’s demands. This makes them a good option. Rather than having a separate MDM system, some of the famous master data management vendors are Informatica master data management and Microsoft master data management.
Master data management has gradually evolved with time by the organizations, the single consolidated truth of data previously practiced as Customer data integration (CDI) and Product Information Management (PMI), which was later combined and further expanded by the MDM. However, they are still active subcategories in some organizations. Identifying all the data domains and subcategories is crucial for having a good set of master data.
MDM implementation might seem a one time process involving some master data management tools. Still, MDM is a technical process and an organizational process, which includes people and dynamic market. This makes the MDM as an ongoing process, in fact some organizations also have MDM centres of excellence (CoEs), the aim of which is to establish, manage and solve any issue in the implementation of the MDM.
Connecting the MDM’s benefits to the overall business strategy and showing how each department will get benefitted by the program is essential to get the buy in from business executives and department heads. This practice should also be aided by including the management and other department executives in the discussion of master data management strategy.

More on Technology